If you like space and DESTRUCTION, you might also like this otherworldly twist from my previous articles. Also, if you want to take a break from school or work and have some time to learn about the great expanse of space, then this article is great for you.
First, let’s talk about planets. If they have life, they will drift away over billions of years losing the energy from its sun because of dark energy. This will then lead to the death of all life on the planet as everything gets as cold as the space around earth.
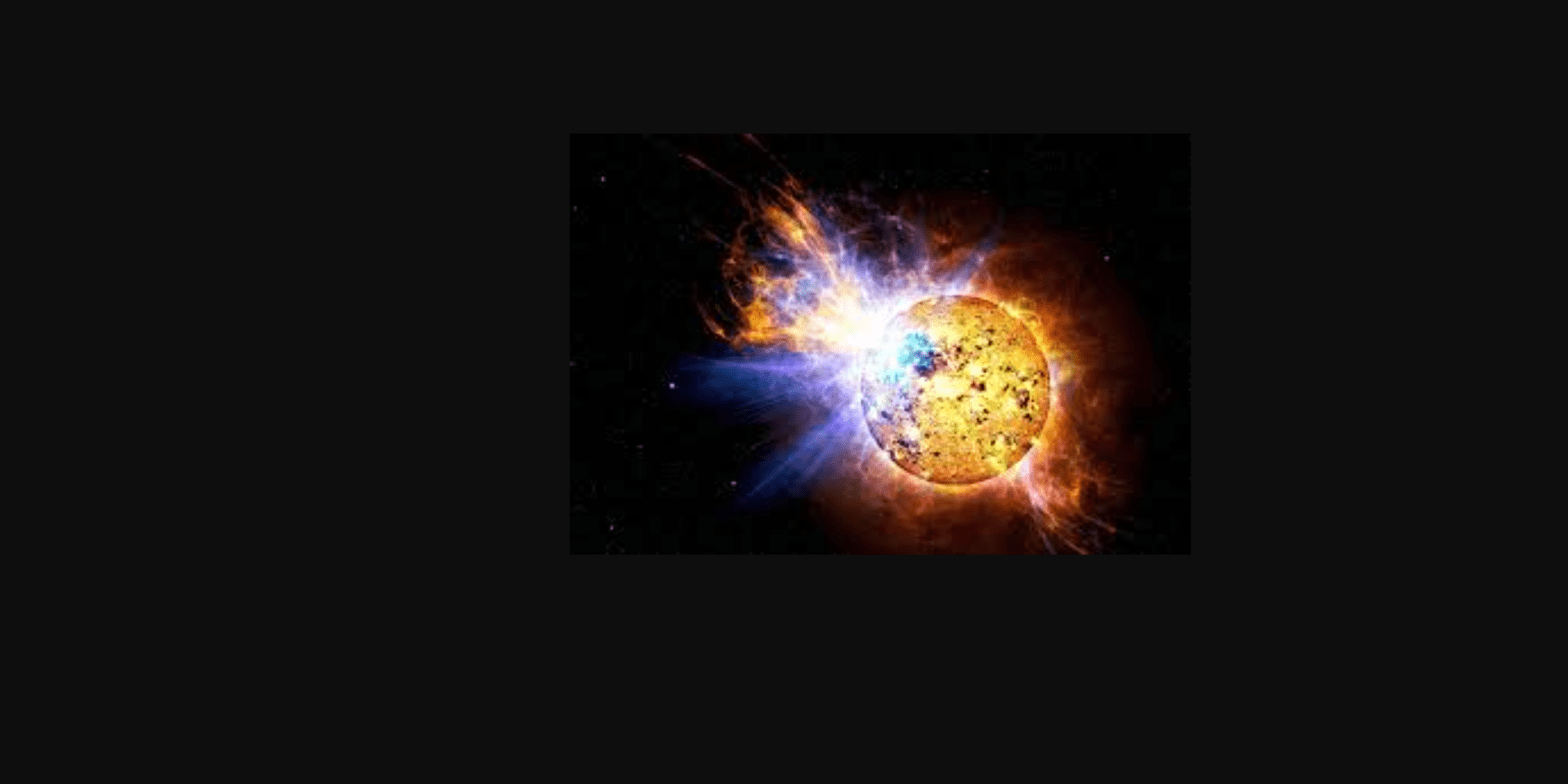
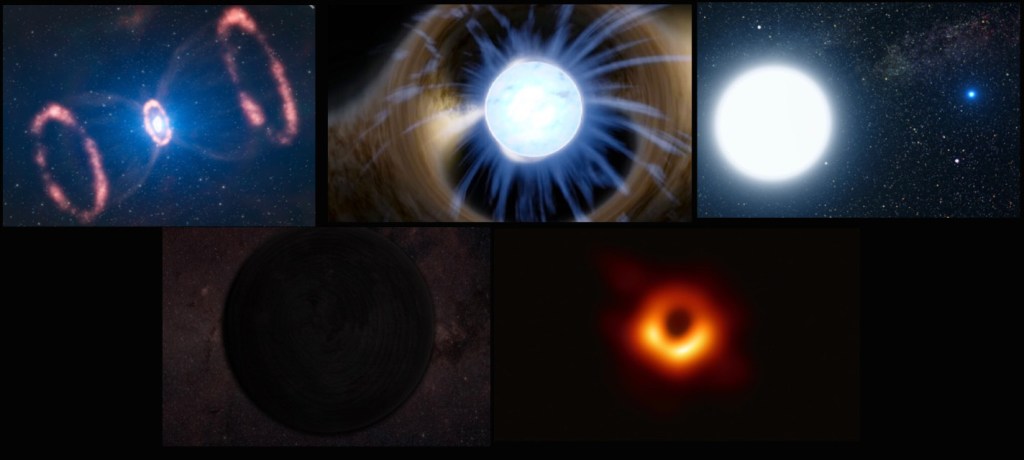
Next, let’s talk about suns and stars. Stars die in a very gruesome way. Imagine getting blown up on the outside and then squished back together very tightly with some of your body still in space. That is basically how stars get destroyed. What’s left is either a black hole when everything is sucked back into the star, or a neutron star that is not quite a black hole, but is also a mind-bogglingly complicated celestial body. But there is another kind of way, some stars like our sun are too small to create a supernova, so our star expands and then retracts and becomes a white dwarf. This then becomes a black dwarf, a hypothetical star that exists after the sun can no longer create energy. Most black holes get destroyed by starving to death. A renowned scientist named Stephen Hawking found out that black holes emit radiation and the combined hot gas that falls out of black holes makes the black hole smaller. Sometimes when a black hole has nothing to gobble up, this process continues and eventually the black hole is tiny or no more.
So I know what you are saying right now. “Hey, what about the rest of the things in the universe? What will happen to them?” This question is answered with “The Big Freeze”. In this event, everything in the universe gets colder and colder until there are no shining stars or planets to make energy in their core, and no black holes to dissolve. After this everything in our universe gets pulled apart by dark energy and particles just float around in the endless expanse of space.

Glossary
- Dark Energy: A theoretical repulsive force that counteracts gravity and causes the universe to expand at an accelerating rate.
- Neutron Star: A celestial object of very small radius (typically 18 miles/30 km) and very high density, composed predominantly of closely packed neutrons. Neutron stars are thought to form by the gravitational collapse of the remnant of a massive star after a supernova explosion, provided that the star is insufficiently massive to produce a black hole.
- Black Hole: a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape.
- Big Freeze/ Heat Death: The heat death of the universe is a theory on the ultimate fate of the universe, which suggests the universe would evolve to a state of no thermodynamic free energy and would therefore be unable to sustain processes that increase entropy.
- White Dwarf: A small very dense star that is typically the size of a planet. A white dwarf is formed when a low-mass star has exhausted all its central nuclear fuel and lost its outer layers as a planetary nebula.
- Black Dwarf: A black dwarf is a theoretical stellar remnant, specifically a white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently that it no longer emits significant heat or light.